Navigating the realm of stainless steel welding unveils a labyrinth of challenges that demand finesse and skill. From combating low thermal conductivity to addressing stress-induced distortions, welders face a myriad of obstacles in achieving seamless joints.
As we explore the intricacies of stainless steel welding issues, we will unravel the complexities that make it a formidable task. Stay tuned to uncover the strategies and solutions employed to master the art of welding this resilient yet demanding stainless steel material.
Stainless steel welding issues presents unique challenges due to its superior thermal conductivity compared to other metals. This necessitates precise control of heat input during welding to mitigate potential distortion and warping of the material.
Moreover, the presence of chromium in stainless steel welding issues can lead to the formation of chromium carbides when reacting with carbon in the stainless steel welding issues electrode. This can render the stainless steel brittle and prone to cracking, posing difficulties in detection and prevention.
Additionally, stainless steel welding issuses 's susceptibility to corrosion underscores the importance of thorough cleaning and protective measures for welded joints to prevent pollution or contamination.
Furthermore, the substantial cost of stainless steel welding issues amplifies the repercussions of errors or rework, both in terms of finances and time.
In conclusion, achieving successful and high-quality welds on stainless steel demands a high level of skill, experience, and meticulous attention to detail.

Stainless steel welding issues presents challenges like warping and cracking due to its low thermal conductivity and high thermal expansion. Additionally, preventing rust formation and managing the complexities of welding dissimilar stainless steels are critical stainless steel welding issues in this process.
Addressing these challenges requires meticulous attention to detail and adherence to best practices to achieve successful welds.
Stainless steel's low thermal conductivity and high thermal expansion make it prone to warping and cracking during welding. To prevent this, balancing heat input is crucial, and using a heat sink like copper or brass can help absorb excess heat.
When addressing the challenges in stainless steel welding issues, one significant concern that arises is the prevention of rust formation, which can impact the integrity and longevity of the welds. Rust prevention is crucial for maintaining the quality of stainless steel welds. Corrosion control, surface protection, oxidation prevention, and metal maintenance are essential aspects to consider when working with stainless steel welding issues to ensure durability and performance. Implementing proper techniques and selecting suitable filler materials can aid in preventing rust formation and maintaining the integrity of the welds. Below is a table highlighting key strategies for rust prevention and corrosion control:
| Key Strategies | Description |
|---|---|
| Rust Prevention | Implementing measures to avoid rust formation |
| Corrosion Control | Techniques to control corrosion processes |
| Surface Protection | Methods to protect the surface from damage |
Despite its corrosion resistance, excessive heat during stainless steel welding can lead to rust formation. Choosing optimal welding parameters and filler alloys can mitigate this risk.
Discover More :
Will 201 stainless steel rust?

Joining different stainless steel grades or dissimilar metals can be difficult due to varying melting points. Careful selection of filler rods and preheating the metals can aid in achieving effective fusion.
Adapting to different welding projects poses unique complexities when working with stainless steel due to its specific properties and requirements. Job transitions in the stainless steel welding issuses field require careful attention to the work environment and workflow optimization to ensure seamless productivity.
Employee training plays a crucial role in equipping welders with the necessary skills to switch between jobs efficiently. Productivity tips such as organizing workstations, preparing equipment in advance, and maintaining a clean workspace can aid in smooth transitions between welding tasks.
In the realm of stainless steel welding issues one critical aspect that demands attention is the mitigation of toxic fumes generated during the welding process. These fumes pose significant health risks to welders and must be carefully managed through proper safety measures.
Key considerations include:
Stainless steel welding method encompasses various methods like TIG, MIG, Shielded Metal Arc, Flux Cored Arc, and Resistance welding.
Each technique offers distinct advantages in terms of stability, speed, cost-effectiveness, uniformity, and cleanliness of welds.
Understanding the differences between these methods is crucial for achieving optimal results in stainless steel fabrication projects. The suitable stainless steel welding methods can avoid more stainless steel welding issues.
TIG Welding Known for its stable arc and precise heat control, TIG welding is widely used in stainless steel fabrication. It offers flexibility with AC and DC polarities but requires consumables like shielding gas and filler rods.
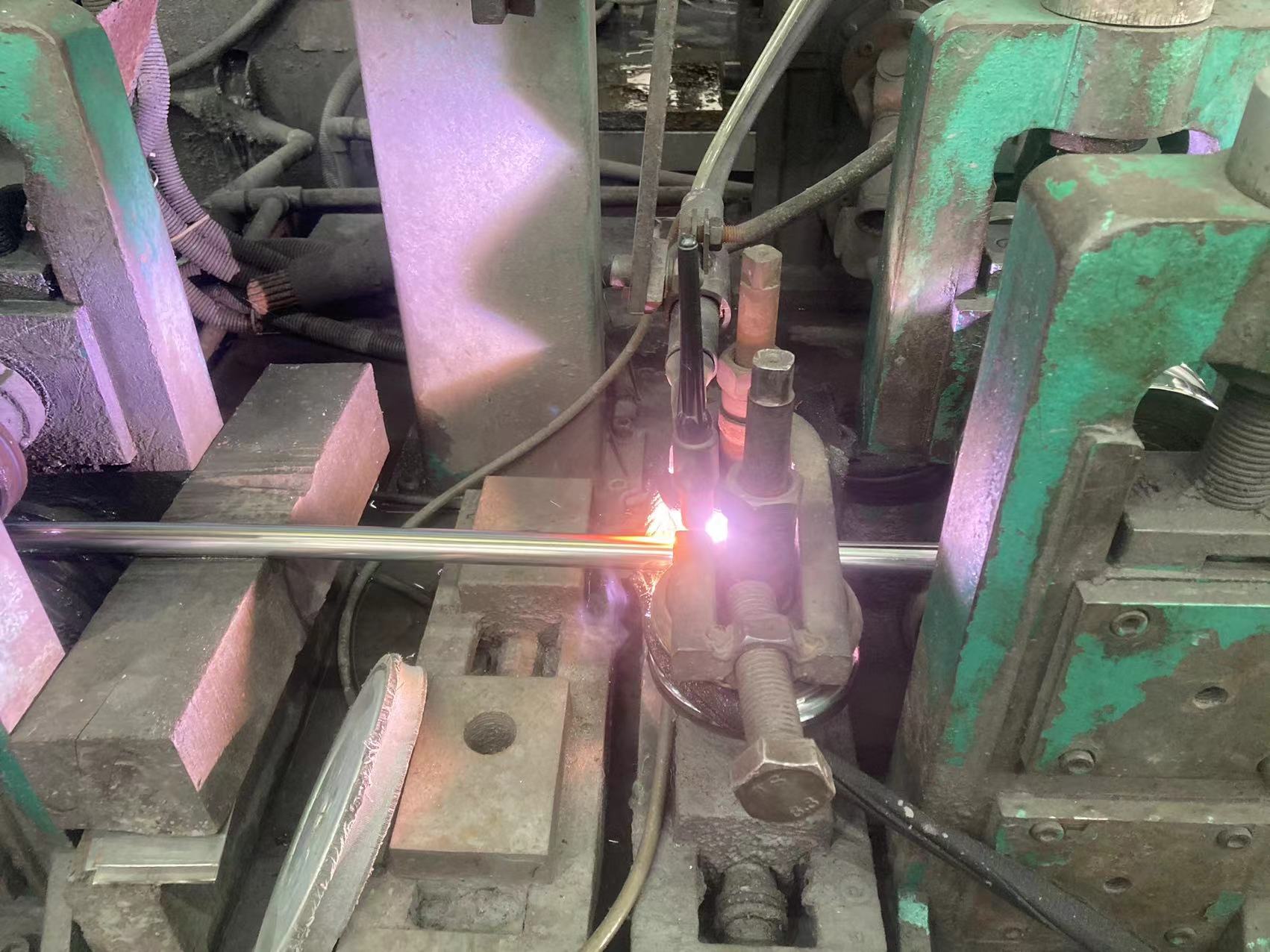
MIG welding Offering faster speeds than TIG welding, MIG welding is favored for its continuous electrode feed. Proper wire feed and cooling techniques are essential to minimize warpage
This cost-effective and portable method is suitable for various repair jobs and outdoor welding. Careful electrode selection is crucial, especially for thicker stainless steel pieces.
The Flux Cored Arc Welding (FCAW) method is a widely utilized technique for welding stainless steel due to its compatibility with shielding gas and ability to produce uniform weld beads. This method is preferred for its efficiency in various welding techniques, especially in stainless steel applications.
The flux core in FCAW helps protect the weld pool from contamination, making it suitable for materials with specific characteristics like stainless steel, known for its temperature resistance. FCAW ensures strong and durable welds, meeting the high standards required for stainless steel projects.
Resistance welding is a commonly employed method in the realm of stainless steel welding, known for its ability to produce clean welds without the need for filler material. When considering this method, several key aspects come into play:
Friction welding emerges as an economical and efficient method for joining stainless steel to carbon steel without the need for consumables. The process offers benefits such as increased productivity, reduced material waste, and enhanced joint strength. Friction welding is particularly suitable for various stainless steel applications where high weld quality and efficiency are crucial.
To optimize the friction welding process, factors like friction pressure, burn-off length, and rotational speed need careful consideration. By following welding efficiency tips and fine-tuning parameters, welders can achieve superior stainless steel weld quality. Overall, friction welding proves to be a valuable technique in the welding industry, providing reliable and cost-effective solutions for joining stainless steel components.
You may also like:
How to Weld Stainless Steel Tubing Like a Pro
The Difference of Stainless Steel Pipe TIG Welding and HF Welding
When considering stainless steel welding issues, it is essential to weigh both the advantages and disadvantages.
Stainless steel offers benefits such as durability, corrosion resistance, and suitability for various industries.
However, challenges like high material cost, difficulty in welding processes, and the risk of chromium carbide formation need to be carefully managed for successful welding outcomes.

When considering stainless steel welding issues, it is essential to acknowledge the numerous advantages.
Stainless steel's exceptional corrosion resistance stands as one of its prominent advantages in welding applications. This resistance is crucial for preventing rust formation and ensuring longevity.
To maximize this benefit, welders should consider various factors such as welding techniques, material properties, surface finishing, and joint design strategies. These elements play a significant role in maintaining the material's integrity and enhancing its resistance to corrosion.
Strength and durability are key attributes that make welding stainless steel a preferred choice for applications requiring robust and long-lasting metal structures. When considering welding techniques, material properties, joint design, filler selection, and heat control, stainless steel stands out for its resilience and strength. The table below highlights how these factors contribute to the strength and
| Factors | Importance |
|---|---|
| Welding techniques | High |
| Material properties | Essential |
| Joint design | Critical |
| Filler selection | Key |
| Heat control | Vital |
The visual allure of welding stainless steel lies in its ability to exude a sleek and modern aesthetic.
Due to its remarkable properties, welding stainless steel offers a unique advantage in terms of heat and fire resistance. Stainless steel's excellent thermal management capabilities make it suitable for high-temperature applications.
Despite welding challenges such as material properties affecting heat control, safety precautions like advanced techniques ensure successful welds. By employing proper thermal management and advanced techniques, stainless steel welding can achieve superior heat and fire resistance.
Welding stainless steel presents a significant challenge in managing heat sensitivity, impacting the overall welding process and final weld quality.
Specialized equipment and skills play a pivotal role in overcoming the challenges associated with welding stainless steel. Welding equipment designed for stainless steel, specialized skills, stringent quality control measures, and adherence to safety protocols are essential.
The material cost for stainless steel is high, making mistakes costly. Attention to detail, expertise, and precision are crucial for successful welding outcomes, ensuring durability and quality welds.
Cost considerations play a significant role in the welding of stainless steel, impacting both the process efficiency and overall project expenses.
When welding stainless steel, one significant drawback to consider is the risk of contamination, which can impact the integrity and quality of the weld joints. Contamination control, proper welding environment, careful material handling, thorough surface preparation, and adherence to correct welding procedures are essential to prevent issues.
Maintaining strict protocols in these areas is crucial for achieving high-quality welds in stainless steel projects.
Welders working with stainless steel face unique safety concerns due to potential exposure to toxic fumes, UV radiation, and the risk of electric shock. To protect themselves, welders should ensure proper ventilation, wear appropriate personal protective equipment, and consider using safer stainless steel grades with lower chromium content.
Implementing safety measures like forced ventilation and orbital welding technology can mitigate risks and promote a safer welding environment when working with stainless steel.

In the realm of stainless steel welding, welders engaged in working with this material face significant safety concerns that warrant careful attention and precautionary measures. When dealing with stainless steel, welders are at risk due to various factors:
To ensure safety while working with stainless steel during welding, it is imperative to adhere to strict protective measures. Welders who work with stainless steel are exposed to various risks, including toxic fumes, UV radiation, and electric shock. By implementing proper safety protocols, welder health can be safeguarded. Utilizing protective gear, maintaining ventilation control, and ensuring efficient fume extraction are crucial steps in minimizing potential hazards. Below is a table highlighting key protective measures to consider:
| Protective Measure | Importance |
|---|---|
| Protective Gear | Shields against direct contact |
| Ventilation Control | Minimizes exposure to fumes |
| Safety Protocols | Guides safe work practices |
Employing appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) is paramount for ensuring the safety of welders during stainless steel welding processes. When it comes to wearing PPE, consider the following:
By establishing distinct welding workstations, stainless steel welders can enhance safety measures and operational efficiency. Ensuring welding efficiency, material compatibility, joint integrity, welding precision, and process optimization are crucial for successful stainless steel welding. Here is a table highlighting key factors to consider in separate welding operations:
| Factors | Description | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Welding Efficiency | Enhancing productivity | Ensuring timeliness |
| Material Compatibility | Selecting appropriate materials | Preventing defects |
| Joint Integrity | Ensuring strong weld connections | Preventing failures |
| Welding Precision | Achieving accurate welds | Ensuring quality |
| Process Optimization | Streamlining welding operations | Maximizing results |
Implementing these considerations in separate welding operations can lead to safer and more efficient stainless steel welding practices.
When ensuring the success of separate welding operations for stainless steel, it becomes imperative to prioritize the selection of the safest material for welding applications.
Utilizing orbital welding technology enhances safety and precision in stainless steel welding operations. Orbital welding benefits include consistent weld quality, reduced operator error, and efficient automation. This technique finds applications in industries requiring high-quality, high-purity welds, such as pharmaceutical, food processing, and semiconductor manufacturing.
However, orbital welding also presents challenges like initial setup costs, complex equipment maintenance, and limited access in confined spaces. To overcome these challenges, welders must be trained in orbital welding techniques, including proper equipment assembly, parameter setting, and troubleshooting common issues.
Recent orbital welding advancements focus on improved control systems, enhanced data monitoring, and integration with digital technologies for seamless operation and quality assurance.
When it comes to welding stainless steel, adhering to best practices is crucial to ensure safety and quality welds.
Key points to consider include the importance of thorough preparation, selecting the appropriate shielding gas, and techniques to prevent warping and distortion during the welding process.
Effective preparation is crucial for ensuring safety and success in welding stainless steel. To achieve optimal results, consider the following key aspects:
To ensure safety and success in welding stainless steel, one crucial aspect is selecting the appropriate shielding gas, which plays a vital role in protecting the weld pool and enhancing overall weld quality. When choosing the right shielding gas, factors like gas selection, welding parameters, heat control, filler material, and shielding techniques are essential for achieving optimal results.
| Gas Selection | Welding Parameters | Heat Control |
|---|---|---|
| Argon | Voltage | Preheat |
Preventing warping is a critical consideration in ensuring the safety and quality of stainless steel welding practices。
Cutting stainless steel requires precision and adherence to safety protocols to ensure efficient and effective welding practices. When cutting stainless steel, utilizing proper techniques is crucial. Precision cutting methods, careful selection of cutting tools, and finishing edges smoothly are paramount. The table below outlines essential stainless steel cutting techniques, precision cutting methods, metal fabrication tips, cutting tool selection, and the importance of achieving smooth edge finishing.

| Stainless Steel Cutting Techniques | Precision Cutting Methods | Metal Fabrication Tips |
|---|---|---|
| Optimal cutting speed | Use of laser cutting | Clean the work surface |
| Minimize heat input | Waterjet cutting | Secure workpiece firmly |
| Employ coolant for heat control | Plasma cutting | Regular tool maintenance |
| Avoid excessive pressure | Abrasive cutting | Check tool sharpness |
| Monitor cutting depth | Shearing | Wear appropriate PPE |
To ensure successful welding of stainless steel, careful material selection, meticulous joint preparation, proper shielding gas usage, precise heat control, and thorough post-weld cleaning are paramount. Avoiding these common mistakes enhances weld quality and longevity.
The composition of stainless steel significantly impacts the welding process. Factors like heat control, gas coverage, filler selection, joint preparation, preheating, post-weld treatment, welding speed, shielding gas, interpass temperature, and back purging play vital roles in ensuring successful welds.
Implementing precise heat control, filler selection, and back purging techniques are crucial for preventing distortion and cracking in stainless steel welding. Preheating, stress relief, and strategic joint design are vital for maintaining quality welds.
When considering welding different grades of stainless steel, key factors include heat control, filler selection, joint preparation, shielding gas, and post-weld cleaning. Attention to these aspects ensures successful welds with the desired properties and integrity.
To ensure proper ventilation and safety measures when working with stainless steel, welders should prioritize welding fume extraction, wear appropriate personal protective equipment, consider ventilation system design, and adhere to welding fume exposure limits for a safe working environment.
Mastering the Art of 201 Stainless Steel Welding
Mastering Sanitary Stainless Steel Welding: Techniques And Tips
Stainless Steel Pipe Welding Standards: Key Guidelines
In conclusion, stainless steel welding issues is akin to navigating a complex labyrinth, requiring precision, expertise, and specialized techniques to overcome its unique challenges.
Like a skilled navigator, welders must carefully maneuver through the intricacies of low thermal conductivity and high thermal expansion to achieve optimal results.
By understanding the metallurgical processes and employing advanced welding methods, welders can forge durable and corrosion-resistant welds in stainless steel.



