The classification of 304 stainless steel surgical grade is a subject that demands meticulous consideration and analysis within the medical device industry. While renowned for its corrosion resistance and mechanical properties, the designation of 304 stainless steel as suitable for surgical applications is not without debate.
Questions surrounding its biocompatibility, durability under sterilization processes, and long-term performance in the human body persist. Understanding the nuances and intricacies that underpin this classification is crucial for professionals seeking to make informed choices in material selection for critical healthcare instruments and implants.
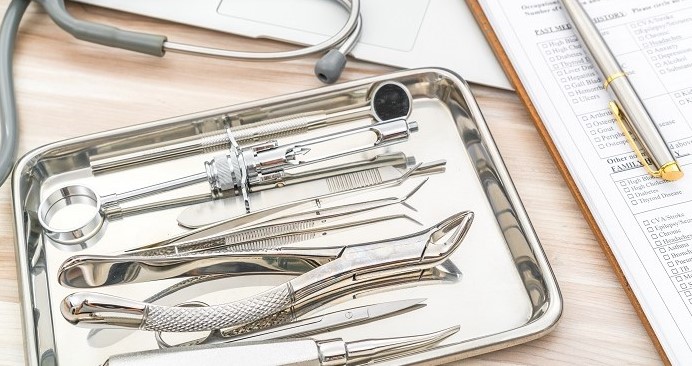
Surgical steel, unlike traditional stainless steel, is specifically formulated for medical applications. It contains higher levels of chromium and sometimes nickel to enhance corrosion resistance and reduce brittleness.
Understanding the differences between surgical steel and stainless steel is crucial in medical device manufacturing. This ensures optimal performance and safety.
Questions regarding the rust resistance, self-healing properties, and staining susceptibility of surgical steel compared to stainless steel are essential considerations for medical professionals and manufacturers.
Containing specific alloying elements that set it apart from traditional stainless steel, surgical steel is distinguished by its enhanced corrosion resistance and reduced brittleness. Surgical steel, with at least 13% chromium and 0.2% carbon, exhibits superior corrosion resistance, making it ideal for surgical applications where durability is paramount.
The addition of nickel in surgical steel not only enhances its resistance to corrosion but also reduces brittleness, ensuring the material can withstand the demands of surgical procedures. These characteristics make surgical steel a preferred choice for medical instruments, implants, and other surgical tools where high performance and reliability are essential.
Material selection, particularly considering nickel content and brittleness reduction, plays a crucial role in the effectiveness of surgical steel in various medical applications.
Stainless steel designated for surgical applications is engineered to resist rust and corrosion effectively. 304 stainless steel surgical grade, known for its exceptional corrosion resistance, is carefully crafted with properties like a minimum of 13% chromium and 0.2% carbon to prevent rust.
This material selection esures durability in various surgical applications where maintaining sterility is paramount. The composition of surgical steel also incorporates nickel to enhance corrosion resistance while reducing brittleness.
When considering materials for surgical instruments or implants, the ability of 304 stainless steel surgical grade to withstand rust is a critical factor. With its superior rust prevention and corrosion resistance, 304 stainless steel surgical grade remains a top choice in the medical field for its reliability and longevity.
You may also like:
Will 201 Stainless Steel Rust?
Understanding Stainless Steel Tube Corrosion and How to Prevent It
304 stainless steel surgical grade is a specialized material engineered to resist rust effectively.
This stainless steel material's selection is critical for ensuring the longevity and effectiveness of medical devices, highlighting the importance of considering factors like durability and corrosion resistance for optimal long-term performance.
The magnetic properties of 304 stainless steel surgical grade are often a point of discussion within the realm of material science and medical device manufacturing.
304 stainless steel surgical grade's non-magnetic nature, combined with its corrosion resistance and material properties, makes it a popular choice for various surgical instruments and implants.

In selecting steel of high quality for surgical purposes, one must prioritize properties such as corrosion resistance and biocompatibility. Steel selection for surgical applications requires careful consideration of material standards and compliance with quality standards.
Corrosion resistance is crucial in ensuring the longevity and performance of surgical instruments and implants. 304 stainless steel surgical grade, with its specific composition including chromium and carbon content, meets the stringent requirements of the medical industry.
Adhering to quality standards guarantees the reliability and safety of products used in surgical procedures. When choosing steel for surgical purposes, it is essential to prioritize quality standards to ensure the highest level of performance and patient safety.
Common medical stainless steels include 304, 316, 316L, 420, 440, and 630 stainless steel grades.
Each grade offers unique properties suitable for various medical applications.
Understanding the distinctions between these stainless steels is crucial for selecting the appropriate material for specific medical devices.
304 Stainless Steel is a widely utilized material in various medical applications due to its corrosion resistance and versatility in critical environments.
2.Austenitic Structure: 304 stainless steel is an austenitic alloy, meaning it possesses a face-centered cubic crystal structure at room temperature. This structure contributes to its strength, toughness, and excellent formability, making it easy to fabricate into different shapes.
3. High Temperature Resistance: 304 stainless steel maintains its mechanical properties and corrosion resistance even at elevated temperatures. This characteristic makes it suitable for applications involving stainless steel tube for heat exchanger , such as industrial and automotive components.
4. Ease of Stainless Steel Tubing Fabrication: Due to its austenitic structure, 304 stainless steel is easily formable, allowing for various fabrication processes such as welding, machining, and forming. This versatility makes it a preferred material in the manufacturing of a wide range of products.
5.Hygienic Properties: The corrosion resistance and non-reactivity of 304 stainless steel surgical grade make it an ideal choice for applications in the food and beverage industry, where hygiene and cleanliness are critical.
For more information about 304 stainless steel , please go through our other blog:
Exploring 304 Stainless Steel Welded Pipes
Utilized extensively in medical applications for their enhanced properties, 316L surgical steel and other common medical stainless steels provide crucial durability and corrosion resistance required for critical healthcare environments.
316L surgical steel, known for its high biocompatibility and excellent corrosion resistance, is particularly suited for surgical applications where durability is paramount. Compared to other alloys, 316L stands out for its resistance to crevice and pitting corrosion, making it ideal for use in environments with corrosive chloride gas.
Material selection plays a vital role in ensuring the longevity and reliability of medical devices, with 316L stainless steel often being a preferred choice due to its superior biocompatibility and resistance to harsh chemical environments.
| Alloy Selection | Corrosion Resistance | Material Properties |
| 304 Stainless Steel | High | Non-magnetic, Cold workable |
| 316 Stainless Steel | Very High | Molybdenum for added corrosion resistance |
For more information about 316 stainless steel , you can go through the following article:
The Ultimate Guide to 316 Stainless Steel Welded Pipes
Differences Between 316 and 316L Welded Stainless Steel Pipe
420 Stainless Steel
This particular grade is unsuitable for use as an implantable material. Despite its commendable ductility, it demonstrates exceptional corrosion resistance when in its annealed state, polished, or subjected to hardening or surface grinding, thanks to a minimum chromium content of 12%. Magnetic in both annealed and hardened conditions, Grade 420 is, however, exclusively employed in the hardened state. When hardened, it effectively withstands fresh water, alkalis, air, various foods, and mild acids.
Surgical Steel Grade 420 also exhibits notable strength and impact resistance. Its machining capabilities are noteworthy, attributable to a sulfur content of up to 0.03%.
440 Stainless Steel
Referred to as "razor-blade steel" in medical applications, Grade 440 displays excellent resistance to mild acids, alkalis, foods, fresh water, and air. A smoothly polished surface enhances its corrosion resistance in tempered, passivated, and hardened conditions.
In its annealed state, Grade 440 stainless steel can be easily machined. However, post-hardening machining poses extreme difficulty, and in some cases, may be impossible. The medical industry employs two variations of Grade 440: 440B and 440C, differing primarily in their carbon content. Both boast high carbon levels, with 440C containing a greater amount, rendering this stainless steel challenging to machine.
630 Stainless Steel
Not intended for implant devices, this material offers excellent wear resistance, making it well-suited for surgical instruments. Often referred to as 17-4 due to its composition, Grade 630 comprises approximately 17% chromium and 4% nickel.
Subject to high levels of heat treatment, 630-grade stainless steel attains impressive strength and hardness. It possesses good toughness in both the base metal and welds, minimizing warpage and scaling. While its corrosion resistance mirrors that of 304, its low carbon content ensures excellent mechanical properties.
When comparing 304 and 316 stainless steel, crucial factors come into play. The differences in their chemical compositions influence their heat resistance and corrosion performance, impacting their suitability for various applications.
Understanding the price disparity between 304 and 316 stainless steel is essential when determining the most cost-effective and efficient option for specific needs.
You may also like:
What Is the Difference Between 201 and 304 Stainless Steel?
In comparison to 316 Stainless Steel, the chemical composition of 304 Stainless Steel distinguishes itself through specific alloy elements affecting its corrosion resistance and suitability for various applications.
| Element | 304 Stainless Steel Composition (%) | 316 Stainless Steel Composition (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Carbon (C) | 0.08 | 0.08 |
| Manganese (Mn) | 2.00 | 2.00 |
| Phosphorus (P) | 0.045 | 0.045 |
| Sulfur (S) | 0.030 | 0.030 |
| Silicon (Si) | 0.75 | 0.75 |
| Chromium (Cr) | 18.00 - 20.00 | 16.00 - 18.00 |
| Nickel (Ni) | 8.00 - 10.50 | 10.00 - 14.00 |
| Molybdenum (Mo) | - | 2.00 - 3.00 |
| Nitrogen (N) | - | 0.10 |
The typical use of 304 Stainless Steel, as compared to 316 Stainless Steel, encompasses a wide range of industries and applications due to its specific characteristics and properties.
304 Stainless Steel is known for its excellent corrosion resistance, making it suitable for applications in food & beverage, cryogenic, chemical processes, medical, oil & gas, and marine industries. This grade can achieve high strength through cold working processes. It is commonly used in marine applications due to its resistance to corrosion.
Additionally, super austenitic grades of 304 Stainless Steel, with higher nickel content, offer extreme corrosion and oxidation resistance, making them ideal for demanding environments such as those found in marine and oil & gas industries.

Comparing the heat resistance properties of 304 Stainless Steel to 316 Stainless Steel reveals distinct characteristics that play a crucial role in determining their suitability for specific applications.
Stainless steel grades 304 and 316 are both popular choices, but 316 stainless steel is generally more expensive than 304. This is primarily because 316 contains additional alloying elements, such as molybdenum, which enhances its corrosion resistance, especially in aggressive environments like marine settings. The higher corrosion resistance and additional alloying elements contribute to the increased cost of 316 stainless steel.
To get the most accurate and up-to-date information on the price difference between 304 and 316 stainless steel, it is recommended to check with local suppliers, distributors, or online metal pricing platforms for the latest market rates. Keep in mind that prices can vary, and it's essential to consider factors such as quantity, quality, and specific product requirements when obtaining price quotes.
The prices of stainless steel can vary based on factors such as location, market conditions, and supplier pricing policies. Additionally, prices can change over time due to fluctuations in the global market.

Discover More: Comprehensive Guide to Stainless Steel Tubing Manufacturers Worldwide
In assessing the performance differences between 304 and 316 stainless steel for various applications, a detailed examination of their unique properties and corrosion resistance capabilities is essential.
Material selection: The choice between 304 and 316 stainless steel depends on the specific application requirements, such as the need for increased corrosion resistance or specific environmental conditions.
You may also like:
304 VS 316 Stainless Steel Sanitary Tubing
Comparing 201 Stainless Steel Welded Pipes to 304 Stainless Steel Welded Pipes
The carbon content in surgical steel influences its properties compared to other stainless steels. Higher carbon content can enhance strength but may reduce corrosion resistance. It can also impact hardness and flexibility, affecting the material's ductility.
Weldability and machinability are influenced by the steel's composition, with higher carbon levels potentially affecting these characteristics. Balancing carbon content is crucial for achieving desired properties in surgical steel for various applications.
Regulatory compliance dictates the classification of 'surgical grade' stainless steel, focusing on specific chromium and nickel content to ensure corrosion resistance and durability for medical implant materials. Carbon content influences properties such as strength and ductility.
Advancements in material science have led to nickel-free alternatives like BioDur 108. Understanding these standards is crucial for ensuring safety, reliability, and compliance with medical device regulations.
When considering the suitability of materials for permanent implant devices, factors such as:
must be taken into account.
While surgical stainless steel may offer some advantages, other materials like titanium or certain medical-grade plastics may be more suitable due to their specific properties and performance characteristics in medical applications.
Nickel's presence in surgical steel impacts its performance and durability in medical applications by reducing brittleness and enhancing corrosion resistance.
Understanding material properties, including carbon content and regulatory standards, is crucial for ensuring implant safety.
Alternative materials like BioDur 108 offer nickel-free options.
Advancements in medical-grade steels provide benefits such as improved safety and compliance.
Incorporating these factors ensures optimal performance and durability of surgical steel in medical settings.
Advancements in medical-grade stainless steels have focused on enhancing corrosion resistance, tensile strength, and biocompatibility for surgical use. Innovations include alloys with improved flexibility and hardness, crucial for medical applications.
These developments aim to optimize sterilization processes and reduce allergies, ensuring greater patient safety. Continuous research and material advancements in the field offer promising benefits for improved properties in medical-grade stainless steels, catering to the evolving needs of surgical procedures.
What Is Food Grade 304 Stainless Steel?
Mastering 304 Stainless Steel Square Tubing: Complete Guide
Exploring the Versatility and Durability of 304 Stainless Steel Round Tubing: A Comprehensive Guide
In conclusion, the designation of 304 stainless steel as surgical-grade material is supported by its exceptional corrosion resistance, mechanical properties, and versatility.
While other stainless steel grades like 316 also offer benefits for medical applications, the specific attributes of 304 make it a viable choice for surgical instruments and implants.
Careful consideration of the material properties and requirements of each medical device is essential in ensuring optimal performance and safety in healthcare settings.



